DALLAS AND PLANO TEXAS BACK PAIN DOCTOR
BACK PAIN RELIEF & MANAGEMENT
Home » Conditions » Back Pain & Low Back Pain
CENTERS & INSTITUTES
Outnumbered by respiratory infections, back pain is one of the most commonly cited reasons that Americans have to go to the doctor or miss work. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, back pain and lower back pain is also a leading cause of disability worldwide, with around 80% of people experiencing it at least once in their lifetime. Back pain management is a growing field that can have great benefits & success if a doctor is consulted for natural treatment procedures before further, more serious alternatives.
Men and women are equally affected by lower back pain which can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp sensation and can leave the person incapacitated. Pain can begin abruptly as a result of an accident or by lifting something heavy, or it could develop over time because of age-related changes in the spine. Sedentary lifestyles could also set the stage for lower back pain, especially when a routine of too little exercise is punctuated by a rigorous weekend workout.
Types of Back Pain
Acute Back Pain
Most lower back pain is considered acute, or short-term, and it can last a few days up to a few weeks. This type of back pain tends to resolve on its own with self-care, and there is no residual loss of function. The majority of acute back pain is mechanical in nature, meaning that it was caused by the way the components of the back (the spine, muscle, intervertebral discs, and nerves) fit together and move in the course of everyday life.
Subacute Back Pain
Subacute lower back pain is defined as pain that lasts between 4 and 12 weeks, whereas chronic back pain is defined as pain that persists for 12 weeks or longer, even after an initial injury or underlying cause of the back pain has been treated. About 20% of people affected by acute lower back pain develop chronic lower back pain with persistent symptoms after only one year. In some cases, treatment can successfully relieve chronic lower back pain; in other cases, the pain may persist despite medical treatment.
Chronic Back Pain
Recurring back pain resulting from improper body posture is often preventable by properly lifting objects and trying to avoid movements that strain the back. Many work-related injuries are caused or aggravated by activities like heavy lifting, repetitive motions, and bad posture. Using ergonomically designed furniture and equipment can help protect the body from injury while at home and in the workplace, and may reduce the risk of potential back injuries.
Risk Factors for Chronic Back Pain
Age
The first instance of lower back pain usually occurs between the ages of 30 and 50, and back pain becomes more common with old age. As people grow older, the loss of bone strength due to osteoporosis can lead to fractures, reduced muscle elasticity, and tone decrease. The intervertebral discs start to lose fluid and flexibility with advancing age, decreasing their ability to cushion the vertebrae, along with the risk of spinal stenosis.
Physical Health
Back pain is more common among those who do not regularly engage in physical activity. Although it’s easy to add unwanted body fat, unnecessary stress on the back can be from poor eating habits & simply being overweight, often leading to lower back pain. Studies show that low-impact aerobic exercise is beneficial for maintaining the integrity of intervertebral discs and can protect against developing chronic back pain.
Mental Health
Pre-existing mental health issues such as anxiety and depression could actually play a role in how closely one focuses on their back pain, as well as their perception of its severity level. Back pain that becomes chronic could also contribute to the development of even greater psychological factors. Mental stress may affect the body in numerous ways, including muscle tension, which can lead to more serious health consequences.
Genetics
Some causes of back pain, such as ankylosing spondylitis, a form of arthritis that involves fusion of the spinal joints leading to some immobility of the spine, are often caused by genetic factors that can’t be mitigated as easily as body posture and weight gain.
Occupation
Having a job that requires a great deal of heavy lifting, pushing, or pulling, especially when it involves twisting or vibrating the spine, can often lead to lower back injury and/or other pain. In addition, an occupation that not involve any or much activity, such as a desk job, can also lead to back pain, especially if you have poor posture or sit in a chair most of the day without proper back support.
What Causes Chronic Back Pain?
Back pain is something that affects almost all of us at some point in our lives. However, chronic back pain, pain in the back that lasts for an extended period of time, is not something we all experience. For those that do, it is a very uncomfortable experience and a sometimes debilitating ailment. There are many causes for chronic back pain:
Physical Trauma
One of the most common causes of chronic back pain is due to some sort of physical trauma, such as a car wreck. These types of accidents can result in all sorts of problems that will affect your for a long time. Ruptured discs, torn or pulled muscles and ligaments and even the scar tissue that develops during the healing process can cause problems for people. These types of issues can haunt people for long periods of time. Severely damaging a disc in your back is something that will give you pain for an extended period of time, as it does not heal quickly and most of the time does not return to the same condition as before the injury. People with injuries such as these should work closely with their doctor and make sure they are getting the best help possible to try and prevent or ease any chronic pain that may arise.
Bad Posture
Posture can also be a huge cause of chronic back pain. One common misconception people have is that posture only matters when you’re sitting or standing. This isn’t true. Posture matters no matter what you’re doing. You want to have good posture, especially when it comes to physical activities such as lifting heavy objects or playing sports. Poor posture can lead to a breakdown of connective tissues, leave you at risk for injury to your spine and muscles and spinal degeneration.
Breakdown of Connective Tissue
Chronic back pain can also be a result of the breakdown of connective tissue in the spine. When these tissues break down, there isn’t as much padding as needed, and bones tend to rub against each other. This type of rubbing or grinding causes severe pain for people and is very hard to treat. This is also common in patients with severe injuries to their back because the scar tissue that helps in the healing process isn’t as elastic and padded as normal connective tissue, which means it cannot withstand the day-to-day activities as easily.
Disease
The other major cause of chronic back pain is disease. There are several diseases that can contribute to back problems. Diseases such as scoliosis, osteoporosis, spinal stenosis and sciatica can all contribute.
- Scoliosis is a curvature of the spine that starts affecting people early on in life. It can be quite severe and result in correctional surgery, but most cases are mild and do not require treatment.
- Osteoporosis is a disease that causes a breakdown of the bones, resulting in brittleness of the bones. The potential for this disease increases with age and it is especially high for white and Asian women after menopause.
- Spinal stenosis is a disease resulting in the narrowing of the spinal canal that causes pressure on the spine. This added pressure can be the source of some very severe pain for those suffering from spinal stenosis.
- Sciatica is pain related to the sciatic nerve, which runs from your lower back down through your legs. Sciatica is usually a result of a herniated disc or bone spurs and can be treated effectively within three weeks. However, some cases of sciatica last several weeks, if not months, and can result in corrective surgery.
All of these ailments are very serious. If you are experiencing these chronic back pain symptoms you should seek professional help from our Plano back pain specialists right away. Although some symptoms cannot be cured, pain management and coping techniques do exist to help make your life as easy and manageable as possible.
How is Back Pain Diagnosed?
Physical Exam
A complete medical history and physical exam early on can help to identify any serious conditions that may be causing the pain. During the exam, Dr. Rodriguez will ask about the source and severity of your back pain, duration of symptoms, and any previous health conditions that might be related to the pain. Along with a thorough back examination, he may conduct brain exams. The cause of chronic lower back pain may still be difficult to determine, even after a thorough neurological examination.
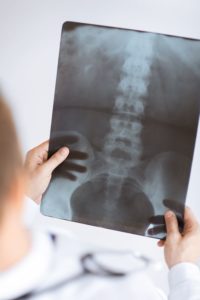
X-Ray
Imaging tests are not warranted in most cases of lower back pain treatment. Under certain circumstances, Dr. Rodriguez may use an X-ray to rule out specific causes of pain. X-rays show the bony structures and any vertebral misalignment or fractures. Soft tissues, such as muscles, ligaments, or bulging discs are not visible on conventional x-rays.
CT Scan
Computerized tomography scans are often used to see spinal structures that cannot be seen on conventional x-rays. Using a computer, the CT scan creates a three-dimensional image from a series of two-dimensional pictures.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is a noninvasive way to identify a condition that may require immediate surgical treatment. MRI scans can also produce images of soft tissues, such as muscles, ligaments, tendons, and blood vessels. Dr. Rodriguez considers MRIs if he suspects a serious problem, like infection, tumor, inflammation, disc herniation or rupture, or pressure on a nerve.
Lower Back Pain
Lower back discomfort is a health condition that many experiences at some time in their lives. Lower back discomfort begins below the ribcage and can be intense. It is important to keep in mind; lower back discomfort often gets better on its own; however, when it doesn’t, there are a variety of treatments that can be applied.
What Causes Lower Back Pain?
There are a variety of causes for lower back pain; one of the most common causes is muscle strain/sprain. A strain is when there is a tearing of a muscle or tendon. A sprain is when a ligament is torn. Another cause of lower back discomfort is a bulging and ruptured disc. Osteoarthritis of the spine is another cause of lower back discomfort.
Lower Back Pain Statistics
There are several interesting but unnerving statistics of lower back pain, such as preventing many from working, as well as other everyday activities and being the most common reason why many suffer from sleep loss. In addition, over 250 million people lost work days in one year and experts estimate that 80 percent of the population of the U.S. will experience back discomfort at some time in their lives.
How to Prevent Lower Back Pain?
Millions of people suffer from lower back pain every day; at least four out of five people experience back pain at some point in their lives. Ways to prevent lower back pain are getting more regular exercise, watching your weight, stop smoking, sleeping on your back or side, talking with your doctor and be mindful of your posture, especially when sitting at a desk. Other ways to prevent lower back pain are improving your posture, wearing comfortable shoes and stretching on a regular basis.
What are Symptoms of Lower Back Pain?
Common symptoms of lower back discomfort are a dull aching sensation in the lower back, a stabbing or shooting pain that can radiate down the leg to the foot, an inability to stand up straight without pain or a decrease in range of motion.
- Symptoms of back soreness are often short-lived but can last for days or week.
- Back pain symptoms that may indicate serious problems are the loss of bowel or bladder control, fever or numbness, tingling or weakness in one or both legs.
What are Risk Factors for Lower Pain?
There are several risk factors for back discomfort such as working in a sedentary environment, not exercising, engaging in high-impact activities without stretching or warming up, being older, obese, smoking and being diagnosed with a certain health condition like arthritis.
How is Lower Back Pain Diagnosd?
For lower back pain, Dr. Rodriguez will discuss with you about your symptoms, give you an examination and then decide if other diagnostic tools are necessary to evaluate your condition. Diagnostic tools that are used for this purpose are x-rays, MRIs or CT scans, blood tests, bone scan or nerve studies such as an EMG.
How is Lower Back Pain Treated?
In most cases, back soreness gets better in a few weeks. However, if the pain persists, over-the-counter pain relievers and using heat may help.
- Light activities like walking may help as well as muscle relaxants, topical pain relievers, narcotics.
- Antidepressants and injections like cortisone.
- In addition, your doctor may also suggest physical therapy.
- Physical therapy such as heat, ultrasound and electrical stimulation, provide relief for some.
- Alternative medicine are chiropractic care, acupuncture, massage and Yoga.
Dallas Back Pain Treatment
Treatment for low back pain generally depends on whether the pain is acute or chronic. In general, surgery is recommended only if there is evidence of worsening nerve damage and when diagnostic tests indicate structural changes for which corrective surgical procedures have been developed. The Pain Relief Center is cautious about giving prescription pain medication (unless it’s after a surgery), and we often recommend minimally invasive surgery and therapeutic approaches before prescribing potentially harmful medication.
You may even find success in other methods of pain management, such as TENS machines. But, can you overuse a tens unit? How high should you set it? Speak with a pain management specialist to determine what is best for you.
We perform the following treatments for lower back pain relief:
More Conditions
- Achilles Tendinitis
- Allergies
- Arthritis
- Back Pain & Low Back Pain
- Bulging Disc
- Car Accident Injuries
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Cervicogenic Headache
- Chronic Pain
- Cluster Headache
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Fibromyalgia
- Foot Pain
- Interstitial Cystitis
- Joint Pain
- Knee Pain
- Low Estrogen
- Neck Pain
- Occipital Neuralgia
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Piriformis Syndrome
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Rotator Cuff Tear
- Sacroiliitis Pain
- Sciatica
- Scoliosis
- Shingles
- Shoulder Pain
- Spinal Pain
- Spinal Stenosis
- Tension Headache
- Thoracic Pain
- TMJ
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
TAKE ACTION
The most critical step on the path to recovery is finding a pain management doctor who can address your pain management needs successfully. The Pain Relief Center and its five specialized institutes are dedicated to meeting any and all of a patient’s needs. Located in the Dallas-Fort Worth area, Dr. Rodriguez and his friendly staff will help you along the path to recovery.
Our new center in Dallas is part of a nationwide development by Pain Relief Centers, geared to providing individualized and comprehensive healing and pain management services with unprecedented levels of compassion, care, and comfort for each patient.

